No products in the cart.

Nutrient Cycling: Understanding Nature’s Recycling System
Nutrient Cycling: Understanding Nature’s Recycling System
Nutrient cycling is like nature’s own recycling program. Have you ever wondered how the nutrients essential for life on Earth are constantly replenished and reused? In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of nutrient cycling, exploring its importance, processes, and impact on our environment.
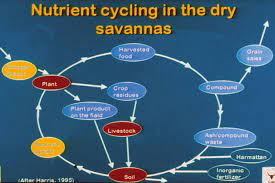
Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
|---|---|
| 1. | What is Nutrient Cycling? |
| 2. | Importance of Nutrient Cycling |
| 3. | Types of Nutrient Cycles |
| 4. | The Nitrogen Cycle |
| 5. | The Carbon Cycle |
| 6. | The Phosphorus Cycle |
| 7. | The Water Cycle |
| 8. | Human Impacts on Nutrient Cycling |
| 9. | Enhancing Nutrient Cycling in Agriculture |
| 10. | Nutrient Cycling in Forest Ecosystems |
| 11. | Climate Change and Nutrient Cycling |
| 12. | Conclusion |
| 13. | FAQs about Nutrient Cycling |
What is Nutrient Cycling?
Nutrient cycling is the process where nutrients move through the environment in various forms from the air, soil, water, organisms, and back into the environment. It’s essentially nature’s way of recycling nutrients so that they can be used again and again.
Importance of Nutrient Cycling
Nutrient cycling is crucial for maintaining life on Earth. It ensures that essential elements like carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and others are available for living organisms to grow and function properly.
Why is Nutrient Cycling Important for the Environment?
Nutrient cycling helps to maintain the balance of nutrients in ecosystems, supporting biodiversity and the stability of ecosystems. Without it, nutrients would become locked away and unavailable, disrupting the delicate balance of life.
Types of Nutrient Cycles
There are several key nutrient cycles that play significant roles in the environment. These cycles involve the movement of nutrients through various reservoirs such as the atmosphere, soil, water bodies, and living organisms.
The Nitrogen Cycle
The nitrogen cycle is vital for the growth of plants and other organisms. It involves processes like nitrogen fixation, nitrification, assimilation, ammonification, and denitrification.
The Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle is crucial for regulating the Earth’s climate and is driven by processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion.
The Phosphorus Cycle
The phosphorus cycle is essential for the formation of DNA, RNA, and ATP, and involves weathering of rocks, phosphate runoff, and assimilation by plants.
The Water Cycle
The water cycle is not just about water—it also involves the movement of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus through the environment, affecting their availability to living organisms.
Human Impacts on Nutrient- Cycling
Human activities such as agriculture, industry, and urbanization can disrupt natural nutrient cycles. For example, excessive use of fertilizers can lead to nutrient runoff into water bodies, causing eutrophication.
How Do Human Activities Affect Nutrient -Cycling?
Human activities can disrupt natural nutrient cycles by altering the flow of nutrients through ecosystems, which can have serious consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Enhancing Nutrient- Cycling in Agriculture
Nutrient- cycling is crucial for sustainable agriculture. Practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and composting can help to enhance nutrient- cycling in agricultural systems.
What Are Some Agricultural Practices That Promote Nutrient -Cycling?
Agricultural practices like crop rotation and cover cropping help to maintain soil fertility and reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers, promoting healthier ecosystems.
Nutrient -Cycling in Forest Ecosystems
Forest ecosystems play a critical role in nutrient -cycling. They act as sinks for carbon and provide habitats for diverse species.
How Do Forests Contribute to Nutrient- Cycling?
Forests recycle nutrients through processes like litterfall, decomposition, and nutrient uptake by trees, contributing to the health and stability of ecosystems.
Climate Change and Nutrient -Cycling
Climate change can have profound effects on nutrient cycles, influencing processes like decomposition rates and nutrient availability.
How Does Climate Change Impact Nutrient -Cycling?
Climate change can alter temperature and precipitation patterns, affecting the rates of nutrient- cycling and the availability of nutrients for plants and other organisms.
Conclusion
In conclusion, nutrient- cycling is essential for maintaining life on Earth. By understanding the processes and importance of nutrient- cycling, we can better appreciate the delicate balance of our ecosystems and work towards preserving them for future generations.
FAQs about Nutrient -Cycling
What is nutrient- cycling?
Nutrient- cycling is the process by which nutrients are recycled through the environment, ensuring their availability for living organisms.
Why is nutrient -cycling important?
Nutrient -cycling is important because it maintains the balance of nutrients in ecosystems, supporting biodiversity and ecosystem stability.
How do humans impact nutrient- cycling?
Humans impact nutrient- cycling through activities like agriculture and urbanization, which can disrupt natural cycles and lead to environmental problems.
What are some examples of nutrient cycles?
Examples of nutrient cycles include the nitrogen cycle, carbon cycle, and phosphorus cycle, which are essential for life on Earth.
How does climate change affect nutrient cycling?
Climate change can affect nutrient cycling by altering temperature and precipitation patterns, which in turn influence the availability of nutrients for plants and other organisms.
Go and turn on towards organic farming to save future and thire save childs:
Elevate Plant Growth with Premium Bone Powder – Buy Now!
Organic Cow Dung Compost: Transform Your Garden Naturally
Premium Humic Acid for Healthy Plants | Enhance Soil & Boost Growth
Boost Plant Growth Naturally with Mustard Cake | Organic Fertilizer
Transform Your Garden with NPK Fertilizer | Boost Growth by 30%
Premium Perlite for Enhanced Gardening | Buy Now
Live Earthworms with Enhance Your Garden (soil health)
1 Neem Khali: Unveiling the Wonders of Nature
1Transform your garden with vermiwash-buy now
1 Premium quality Vermicompost [ केचुआ खाद ]
Follow us:
Tagged Innutrient cycling


[…] our water bodies. But what exactly is the phosphorus cycle, and why should we care? Let’s explore this fascinating cycle and understand why it’s so vital to life on […]