No products in the cart.
Agricultural Practices: Cultivating the Future of Farming
Agricultural Practices: Cultivating the Future
Introduction
Welcome to the world of agricultural practices, where the art and science of growing crops meet the challenges of a changing world. In this article, we’ll explore the fundamental techniques and innovations that shape modern agriculture. From sustainable farming methods to the role of technology in food production, we’ll cover it all in a language that everyone can understand.

Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
|---|---|
| 1 | What are Agricultural Practices? |
| 2 | Importance of Agricultural Practices |
| 3 | Traditional vs. Modern Agricultural Practices |
| 4 | Sustainable Farming Methods |
| 5 | Role of Technology in Agriculture |
| 6 | Soil Health and Management |
| 7 | Water Management in Agriculture |
| 8 | Crop Rotation and Diversification |
| 9 | Pest and Disease Management |
| 10 | Importance of Pollinators |
| 11 | Agricultural Practices and Climate Change |
| 12 | Challenges and Future Trends in Agriculture |
| 13 | Conclusion |
What are Agricultural Practices?
Agricultural practices refer to the various methods and techniques used by farmers to improve crop yield and quality. These practices encompass everything from soil preparation to harvesting and beyond. Farmers worldwide employ diverse strategies to grow different crops, depending on their climate, resources, and market demands.
Importance of Agricultural Practices
Agricultural practices are crucial for ensuring food security and sustainable livelihoods. They not only provide food for the growing global population but also contribute to economic growth and rural development.
Traditional vs. Modern Agricultural Practices
Traditional Practices
Traditional agricultural practices are age-old techniques passed down through generations. These methods often rely on natural fertilizers and manual labor, reflecting local cultural and environmental conditions.
Modern Practices
Modern agricultural practices integrate technology and scientific advancements. They include the use of machinery, synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and biotechnology to increase efficiency and yield.
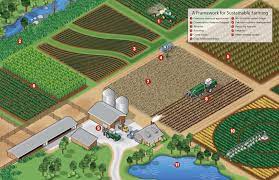
Sustainable Farming Methods
Sustainable farming focuses on maintaining or increasing yields while preserving the environment. Practices like crop rotation, organic farming, and integrated pest management (IPM) minimize the use of synthetic inputs and promote long-term soil health.
Role of Technology in Agriculture
Precision Farming
Precision farming utilizes technology like GPS, sensors, and drones to optimize crop management. Farmers can precisely apply resources like water and fertilizers, reducing waste and environmental impact.
Biotechnology
Biotechnology has revolutionized agriculture through genetically modified organisms (GMOs) that enhance crop resistance, yield, and nutritional content.
Soil Health and Management
Importance of Soil Health
Healthy soils are vital for productive agriculture. Practices such as cover cropping and no-till farming improve soil structure, fertility, and water retention.
Soil Management Techniques
Techniques like composting, mulching, and proper irrigation help maintain soil health and minimize erosion.
Water Management in Agriculture
Water management is critical for sustainable agriculture, especially in arid regions. Techniques like drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting conserve water and optimize its use.
Crop Rotation and Diversification
Benefits of Crop Rotation
Crop rotation prevents soil erosion, improves nutrient availability, and reduces pests and diseases by disrupting their life cycles.
Crop Diversification
Growing a variety of crops on the same land enhances soil health and resilience against climate change and market fluctuations.
Pest and Disease Management
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM combines biological, cultural, and chemical control methods to manage pests while minimizing environmental impact.
Disease Prevention
Crop rotation, resistant crop varieties, and sanitation practices help prevent and manage diseases.
Importance of Pollinators
Pollinators like bees and butterflies are essential for the reproduction of many crops, contributing billions of dollars to agriculture annually.
Agricultural Practices and Climate Change
Climate change poses challenges to agriculture, affecting crop yields, water availability, and pest distribution. Adaptive practices like agroforestry and drought-resistant crop varieties are crucial for resilience.
Challenges and Future Trends in Agriculture
Challenges
Challenges include climate change, soil degradation, water scarcity, and food security issues.
Future Trends
Future trends include precision agriculture, regenerative farming, and the adoption of AI and robotics.
Conclusion
In conclusion, agricultural practices play a pivotal role in feeding the world’s population sustainably. By adopting innovative techniques and respecting traditional wisdom, we can overcome challenges and build a resilient future for agriculture.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What are sustainable farming methods?
Sustainable farming methods aim to maximize productivity while minimizing environmental impact. Techniques include organic farming, crop rotation, and integrated pest management.
2. How does climate change affect agriculture?
Climate change affects agriculture by altering weather patterns, increasing the frequency of extreme events, and shifting the distribution of pests and diseases.
3. Why is soil health important in agriculture?
Healthy soil is vital for plant growth and nutrient uptake. It also contributes to water retention and carbon sequestration, mitigating climate change.
4. What is precision farming?
Precision farming uses technology to optimize crop management, reduce input use, and increase productivity by applying resources like water and fertilizers precisely.
5. How do agricultural practices impact food security?
Effective agricultural practices ensure food security by increasing crop yields, improving food distribution networks, and supporting rural economies.
Go and turn on towards organic farming to save future and thire save childs:
Elevate Plant Growth with Premium Bone Powder – Buy Now!
Organic Cow Dung Compost: Transform Your Garden Naturally
Premium Humic Acid for Healthy Plants | Enhance Soil & Boost Growth
Boost Plant Growth Naturally with Mustard Cake | Organic Fertilizer
Transform Your Garden with NPK Fertilizer | Boost Growth by 30%
Premium Perlite for Enhanced Gardening | Buy Now
Live Earthworms with Enhance Your Garden (soil health)
1 Neem Khali: Unveiling the Wonders of Nature
1Transform your garden with vermiwash-buy now
1 Premium quality Vermicompost [ केचुआ खाद ]
Follow us:
Tagged Inagricultural practices