No products in the cart.
Acidic Fertilizer A Comprehensive Guide for Gardeners
The Essential Guide to Acidic Fertilizer Nurturing Your Garden’s Health
Introduction
Ever wondered why your neighbor’s garden looks so lush and vibrant? The secret could lie in something as simple as the right type of fertilizer. Acidic fertilizers, in particular, are a powerful tool for enhancing plant health and ensuring your garden flourishes. But what exactly are acidic fertilizers, and how can they benefit your plants? Let’s dive in and explore!

Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
|---|---|
| 1 | What is Acidic Fertilizer? |
| 2 | Why Use Acidic Fertilizer? |
| 3 | Types of Acidic Fertilizers |
| 4 | Benefits of Acidic Fertilizer |
| 5 | How to Determine Soil Acidity |
| 6 | How to Apply Acidic Fertilizer |
| 7 | Best Plants for Acidic Fertilizers |
| 8 | Common Mistakes to Avoid |
| 9 | DIY Acidic Fertilizers |
| 10 | Environmental Impact of Acidic Fertilizers |
| 11 | Balancing Soil pH |
| 12 | When to Use Acidic Fertilizer |
| 13 | Comparing Acidic and Alkaline Fertilizers |
| 14 | FAQs About Acidic Fertilizers |
| 15 | Conclusion |
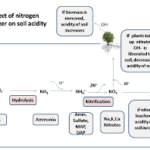
What is Acidic Fertilizer?
Acidic fertilizer is a type of plant food designed to lower the pH level of the soil. Soil pH is a measure of how acidic or alkaline the soil is, and it plays a crucial role in plant health. Most plants thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil, but some plants prefer more acidic conditions. Acidic fertilizers help create the ideal environment for these plants by lowering the soil pH.
Why Use Acidic Fertilizer?
Using acidic fertilizer can be the key to unlocking the full potential of your garden. Do you have azaleas, rhododendrons, or blueberries that just don’t seem to thrive? These plants love acidic soil, and without it, they can struggle. Acidic fertilizers can also help prevent nutrient deficiencies and promote healthy root development.
Types of Acidic Fertilizers
There are various types of acidic fertilizers, each with its unique properties and benefits. Some common types include:
Organic Acidic Fertilizers
These are made from natural materials like peat moss, composted pine needles, and coffee grounds. They not only acidify the soil but also improve its texture and fertility.
Inorganic Acidic Fertilizers
These are synthetic products specifically formulated to lower soil pH. Examples include ammonium sulfate and sulfur-coated urea. They are often more concentrated and act faster than organic options.
Benefits of Acidic Fertilizer
Enhanced Nutrient Availability: Many essential nutrients become more available to plants in acidic soil.
Improved Plant Health: Acid-loving plants thrive in the right soil conditions, leading to healthier, more vigorous growth.
Disease Prevention: Proper soil pH can reduce the risk of certain plant diseases.
Better Root Development: Acidic- fertilizers can promote stronger root systems, which are vital for nutrient uptake and overall plant health.
How to Determine Soil Acidity
Before you start using acidic- fertilizers, it’s essential to know your soil’s current pH level. Here’s how you can do it:
Soil Testing Kits
A soil testing kit is available online or in garden centres. These kits are simple to use and yield results right away.
Professional Soil Testing
For more accurate results, consider sending a soil sample to a professional testing lab. They can provide detailed information about your soil’s pH and nutrient levels.
How to Apply Acidic -Fertilizer
Applying acidic fertilizer correctly is crucial for achieving the best results. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Test Your Soil
Always start by testing your soil to determine its current pH level. This will help you decide how much acidic fertilizer to use.
Step 2: Choose the Right Fertilizer
Select an acidic -fertilizer that suits your plants’ needs. For example, if you’re growing blueberries, opt for a fertilizer specifically designed for acid-loving plants.
Step 3: Apply the Fertilizer
For application rates and procedures, refer to the manufacturer’s instructions.. Typically, you’ll spread the fertilizer evenly around the base of the plants and water it in thoroughly.
Step 4: Monitor and Adjust
Keep an eye on your plants and soil pH. You may need to reapply the fertilizer periodically to maintain the desired acidity.
Best Plants for Acidic -Fertilizers
Not all plants thrive in acidic soil, but many popular garden plants do. Here are some examples:
Azaleas and Rhododendrons: These stunning flowering shrubs prefer acidic soil.
Blueberries: For the best fruit production, blueberries need acidic conditions.
Camellias: These beautiful, evergreen shrubs thrive in acidic soil.
Hydrangeas: The color of hydrangea flowers can change based on soil pH, with more acidic soils producing blue flowers.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Using acidic- fertilizers can be straightforward, but there are some common mistakes to watch out for:
Over-Fertilizing
Using too much acidic -fertilizer can lower the soil pH too much, harming your plants. Always follow the recommended application rates.
Ignoring Soil Testing
Applying acidic- fertilizer without knowing your soil’s pH can lead to imbalances and poor plant health. Always test your soil first.
Using the Wrong Fertilizer
Not all acidic -fertilizers are suitable for every plant. Make sure you’re using a product that meets your plants’ specific needs.
DIY Acidic -Fertilizers
If you prefer a more hands-on approach, you can make your own acidic -fertilizers using common household items:
Coffee Grounds
Used coffee grounds are slightly acidic and can be sprinkled around the base of acid-loving plants.
Vinegar Solution
Use a gallon of water mixed with one tablespoon of white vinegar to water your plants. This can temporarily lower the soil pH.
Peat Moss
Adding peat moss to your soil can increase its acidity and improve its texture.
Environmental Impact of Acidic -Fertilizers
It’s essential to consider the environmental impact of any gardening practice. Acidic- fertilizers can be beneficial, but they must be used responsibly.
Organic vs. Inorganic
Organic acidic- fertilizers are generally more environmentally friendly than their inorganic counterparts. They improve soil health and reduce the risk of chemical runoff.
Responsible Application
Avoid over-fertilizing and follow the recommended application rates. Excess fertilizer can leach into waterways, causing pollution and harming aquatic life.
Balancing Soil pH
Retaining the ideal pH of the soil requires careful balance. While acidic -fertilizers are beneficial for some plants, others may require more neutral or alkaline conditions.
Testing and Adjusting
The proper pH balance must be maintained through routine soil testing.If your soil becomes too acidic, you can raise the pH by adding lime or wood ash.
Rotating Crops
Consider rotating your crops to avoid depleting the soil of specific nutrients and to maintain a healthy pH balance.
When to Use Acidic -Fertilizer
Timing is crucial when applying acidic- fertilizer. Here are some tips:
Growing Season
Apply acidic -fertilizer at the beginning of the growing season to give your plants a strong start.
Specific Plant Needs
Some plants may require additional applications during their growing cycle. Monitor your plants and soil pH to determine the best times for fertilizing.
Comparing Acidic and Alkaline Fertilizers
Understanding the differences between acidic and alkaline fertilizers can help you make better gardening decisions.
Acidic -Fertilizers
These fertilizers lower soil pH and are ideal for acid-loving plants.
Alkaline Fertilizers
These products raise soil pH and are suitable for plants that prefer neutral to alkaline conditions.
FAQs About Acidic -Fertilizers
1. What plants benefit the most from acidic fertilizers?
Plants like azaleas, rhododendrons, blueberries, and camellias benefit the most from acidic fertilizers.
2. How often should I apply acidic fertilizer?
This depends on your soil’s pH and the specific fertilizer you’re using. Regular soil testing will help you determine the right frequency.
3. Can I use coffee grounds as an acidic fertilizer?
Yes, used coffee grounds can be a mild acidic fertilizer. They are best used as a supplement rather than a primary fertilizer.
4. What are the signs that my soil is too acidic?
Signs of overly acidic soil include yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and poor flowering. Regular soil testing is the best way to monitor soil pH.
5. Are organic acidic fertilizers better than synthetic ones?
Organic fertilizers are generally better for the environment and can improve soil health over time. However, synthetic fertilizers can be more effective for quickly lowering soil pH.
Conclusion
Acidic fertilizers are a valuable tool for any gardener looking to optimize their soil and boost plant health. By understanding your soil’s needs and applying the right type of fertilizer, you can create the perfect growing environment for your plants. Remember to test your soil regularly, use fertilizers responsibly, and enjoy watching your garden thrive!
Go and turn on towards organic farming to save future and thire save childs:
Elevate Plant Growth with Premium Bone Powder – Buy Now!
Organic Cow Dung Compost: Transform Your Garden Naturally
Premium Humic Acid for Healthy Plants | Enhance Soil & Boost Growth
Boost Plant Growth Naturally with Mustard Cake | Organic Fertilizer
Transform Your Garden with NPK Fertilizer | Boost Growth by 30%
Premium Perlite for Enhanced Gardening | Buy Now
Live Earthworms with Enhance Your Garden (soil health)
1 Neem Khali: Unveiling the Wonders of Nature
1Transform your garden with vermiwash-buy now
1 Premium quality Vermicompost [ केचुआ खाद ]
Follow us:



