No products in the cart.

Everything You Need to Know About Crop Fertilizer
Everything You Need to Know About Crop Fertilizer
In the world of agriculture, crop fertilizer plays a crucial role in ensuring healthy and bountiful harvests. But what exactly is crop fertilizer, and why is it so important? Whether you’re a seasoned farmer or simply curious about how our food grows, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the essentials of crop fertilization in a way that’s easy to understand.

Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
|---|---|
| 1. | What is Crop Fertilizer? |
| 2. | Types of Crop Fertilizers |
| 3. | How Does Fertilizer Work? |
| 4. | Importance of Using Fertilizers |
| 5. | Organic vs. Synthetic Fertilizers |
| 6. | When and How to Apply Fertilizers |
| 7. | Common Fertilizer Nutrients and Their Functions |
| 8. | Signs of Fertilizer Overuse or Underuse |
| 9. | Environmental Impact of Fertilizer Use |
| 10. | Tips for Choosing the Right Fertilizer |
| 11. | DIY Organic Fertilizers for Home Gardening |
| 12. | Future Trends in Crop Fertilization |
| 13. | Conclusion |
1. What is Crop Fertilizer?
Crop fertilizer is a substance added to soil or plants to provide essential nutrients that may be deficient for optimal growth and productivity. Essentially, it’s like giving plants a balanced meal to thrive on.
2. Types of Crop Fertilizers
There are various types of fertilizers available, including organic and synthetic options. Organic fertilizers are derived from natural sources like compost and manure, whereas synthetic fertilizers are chemically manufactured.
3. How Does Fertilizer Work?
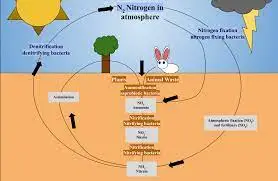
Fertilizers work by replenishing nutrients in the soil that plants need to grow, such as nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium (N-P-K). These nutrients help in various aspects of plant development, from root growth to flower and fruit production.
4. Importance of Using Fertilizers
Using fertilizers is vital for ensuring that plants have access to the necessary nutrients for healthy growth. It can significantly increase crop yields and improve overall plant health.
5. Organic vs. Synthetic Fertilizers
Organic fertilizers are often preferred for their natural composition, which improves soil structure and fertility over time. Synthetic fertilizers, on the other hand, offer more immediate nutrient availability but can have environmental implications.
6. When and How to Apply Fertilizers
The timing and method of fertilizer application are crucial. It’s generally best to apply fertilizers before planting or during key growth stages to maximize nutrient uptake by plants.
7. Common Fertilizer Nutrients and Their Functions
Key nutrients in fertilizers include nitrogen (N), which promotes leafy growth; phosphorus (P), essential for root development; and potassium (K), important for overall plant health and disease resistance.
8. Signs of Fertilizer Overuse or Underuse
Overuse of fertilizers can lead to nutrient imbalances, water pollution, and even harm to beneficial soil organisms. Underuse, on the other hand, can result in nutrient deficiencies and poor plant growth.
9. Environmental Impact of Fertilizer Use
While fertilizers are essential for agriculture, their improper use can lead to environmental issues such as nutrient runoff into water bodies, contributing to algal blooms and ecosystem disruptions.
10. Tips for Choosing the Right Fertilizer
Consider factors like soil type, plant type, and nutrient requirements when selecting a fertilizer. Conduct soil tests to determine specific nutrient deficiencies and choose a fertilizer accordingly.
11. DIY Organic Fertilizers for Home Gardening
For home gardeners looking for natural alternatives, DIY organic fertilizers like compost tea, fish emulsion, and bone meal can be effective and environmentally friendly options.
12. Future Trends in crop fertilizer
The future of crop fertilizer is leaning towards sustainable practices, including precision agriculture, where fertilizers are applied based on real-time data and environmental considerations.
13. Conclusion
Crop fertilizers are fundamental to modern agriculture, ensuring that plants have the nutrients they need to thrive. By understanding the different types of fertilizers and their impacts, farmers and gardeners can make informed choices for better crop yields and environmental sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are the benefits of using crop fertilizers?
Using crop fertilizers can lead to increased crop yields, improved plant health, and enhanced soil fertility, ultimately supporting food production and agricultural sustainability.
2. Can fertilizers harm the environment?
Yes, if not used correctly, fertilizers can contribute to water pollution, soil degradation, and biodiversity loss. It’s important to follow recommended practices to minimize environmental impact.
3. How often should I apply fertilizer to my plants?
The frequency of fertilizer application depends on the plant type and its growth stage. Generally, a soil test can guide you in determining the right timing and amount of fertilizer needed.
4. Are organic fertilizers better than synthetic ones?
Both types of fertilizers have their pros and cons. Organic fertilizers improve soil health in the long run but may be slower acting, while synthetic fertilizers provide quick nutrient availability but can have environmental drawbacks.
5. What happens if plants receive too much fertilizer?
Over-fertilization can lead to nutrient imbalances, burning of plant roots, and environmental pollution. It’s crucial to follow recommended application rates to avoid these issues.
This comprehensive guide should equip you with a solid understanding of crop fertilizers, empowering you to make informed decisions about their use in your own gardening or farming practices. Remember, the key is balance and sustainability for healthy plants and a thriving environment.
mop fertilizer
It seems like you’re asking about “mop fertilizer.” MOP stands for Muriate of Potash, which is a common type of potassium fertilizer used in agriculture. MOP fertilizer contains potassium chloride, a soluble form of potassium that is essential for plant growth.
Potassium is one of the three primary nutrients required by plants, along with nitrogen and phosphorus. It plays a crucial role in many physiological processes within plants, such as photosynthesis, protein synthesis, and water regulation. Potassium also helps plants resist diseases and stresses like drought and cold.
MOP fertilizer is typically applied to crops to correct potassium deficiencies in the soil or to boost potassium levels during critical growth stages. It’s especially important for crops like fruits, vegetables, and grains that require ample potassium for healthy development and yield.
Farmers and gardeners often use MOP fertilizer in granular form, applying it directly to the soil before planting or as a side-dressing during the growing season. The potassium chloride in MOP dissolves readily in soil moisture, making the potassium available for plant uptake.
When using any fertilizer, including MOP, it’s important to follow recommended application rates to avoid overuse, which can lead to nutrient imbalances or environmental issues. Soil testing can also help determine the specific nutrient needs of your crops, ensuring optimal growth and productivity.
banana fertilizer
When it comes to fertilizing banana plants, it’s important to provide the right nutrients at the right time to support healthy growth and fruit production. Bananas are heavy feeders, meaning they require a good supply of nutrients throughout the growing season to thrive. Let’s dive into the specifics of fertilizing banana plants effectively:
Nutrient Requirements for Banana Plants
Banana plants have specific nutrient needs, with potassium (K) being particularly crucial for fruit development. Potassium helps regulate water movement in plant tissues and contributes to fruit quality and yield. In addition to potassium, bananas also benefit from nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) for overall growth and vigor.
Best Fertilizer for Bananas
For optimal growth and fruiting, consider using a balanced fertilizer formulation specifically designed for fruiting plants. Look for a fertilizer with a higher potassium content (the third number on the fertilizer label) to support banana fruit development. A common recommendation is a fertilizer with an N-P-K ratio of approximately 8-10-8 or similar.
Fertilizing Schedule
- Initial Planting: Apply a balanced fertilizer at planting time to encourage strong root establishment.
- Regular Feeding: During the growing season, feed banana plants every 2-3 months with a balanced fertilizer. Avoid applying fertilizer directly to the base of the plant to prevent burning.
Application Method
- Broadcast Application: Spread the fertilizer evenly around the root zone of the banana plant, extending beyond the drip line.
- Incorporation: Lightly incorporate the fertilizer into the top few inches of soil, followed by watering to help nutrients reach the root zone.
Organic Options
If you prefer organic methods, consider using compost, aged manure, or organic fertilizer blends rich in potassium. Organic materials not only provide nutrients but also improve soil structure and microbial activity.
Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
Watch out for signs of nutrient deficiency in banana plants, such as yellowing leaves (indicating nitrogen deficiency) or slow fruit development (indicating potassium deficiency). Adjust your fertilization program accordingly based on plant responses.
Watering After Fertilization
After applying fertilizer, water the banana plants thoroughly to help nutrients penetrate the soil and reach the roots. Adequate moisture is essential for nutrient uptake and plant health.
Conclusion
By providing the right nutrients through timely and balanced fertilization, you can promote robust growth and abundant fruiting in banana plants. Remember to observe your plants’ response to fertilization and adjust your approach as needed. Healthy banana plants will reward you with delicious, tropical fruit!
watermelon fertilizer
Fertilizing watermelon plants properly is essential to ensure healthy growth, vigorous vines, and abundant fruit production. Watermelons have specific nutrient requirements, particularly during different stages of growth, to support their development. Here’s a guide on how to fertilize watermelon plants effectively:
Nutrient Requirements for Watermelon Plants
Watermelon plants require balanced nutrition, with a focus on nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Nitrogen promotes leafy growth and overall plant vigor, phosphorus supports root development and flower formation, while potassium is crucial for fruit development and quality.
Best Fertilizer for Watermelons
Choose a fertilizer with a balanced N-P-K ratio suitable for fruiting plants, such as 5-10-10 or 10-10-10. Watermelons benefit from a steady supply of nutrients throughout their growth cycle, especially during flowering and fruit set.
Fertilizing Schedule
- At Planting: Incorporate a balanced fertilizer into the soil before planting to provide essential nutrients from the beginning.
- During Growth: Side-dress watermelon plants with fertilizer when vines start to run and again when flowers appear. Apply fertilizer several inches away from the plant base to avoid direct contact.
Application Method
- Broadcast Application: Sprinkle fertilizer evenly around each plant, extending beyond the drip line of the vines.
- Topdressing: Gently work the fertilizer into the soil surface without disturbing the roots, followed by watering to help nutrients penetrate the root zone.
Organic Options
For organic gardening, use compost, aged manure, or organic fertilizer blends with a balanced nutrient profile. Organic materials improve soil health and fertility while providing slow-release nutrients to watermelon plants.
Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
Monitor watermelon plants for signs of nutrient deficiency, such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or poor fruit development. Adjust fertilizer applications based on plant response and soil test results.
Watering After Fertilization
After applying fertilizer, water the plants deeply to ensure nutrients reach the root zone. Adequate moisture is essential for nutrient uptake and to prevent fertilizer burn.
Conclusion
By providing the right balance of nutrients at key growth stages, you can optimize watermelon plant health and maximize fruit yield. Remember to tailor your fertilization approach based on plant needs, soil conditions, and environmental factors for successful watermelon cultivation. Happy gardening and enjoy your sweet, juicy watermelons!
Potato fertilizer
Fertilizing potatoes correctly is crucial to achieve healthy growth and a bountiful harvest. Potatoes have specific nutrient needs, particularly during different growth stages, to support their development and tuber formation. Here’s a comprehensive guide on how to fertilize potatoes effectively:
Nutrient Requirements for Potatoes
Potatoes require a balanced supply of nutrients, with a focus on nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). Nitrogen supports leafy growth and overall plant vigor, phosphorus encourages strong root development and tuber formation, while potassium is essential for disease resistance and quality tuber production.
Best Fertilizer for Potatoes
Choose a fertilizer with a balanced N-P-K ratio suitable for root crops, such as 5-10-10 or 10-10-10. Additionally, consider using a fertilizer formulated for acid-loving plants, as potatoes prefer slightly acidic soil conditions.
Fertilizing Schedule
- At Planting: Incorporate a balanced fertilizer into the soil before planting to provide essential nutrients for initial growth.
- During Growth: Side-dress potatoes with fertilizer when plants reach the hilling stage (about 6-8 inches tall) and again when they start flowering. Avoid direct contact with potato stems to prevent burning.
Application Method
- Broadcast Application: Spread fertilizer evenly along the rows or around individual plants, ensuring coverage of the root zone.
- Hilling Technique: Incorporate fertilizer into soil mounds or hilled rows during the growing season to encourage tuber development and nutrient uptake.
Organic Options
For organic gardening, use compost, aged manure, or organic fertilizer blends with a balanced nutrient profile. Organic materials enrich the soil with beneficial microbes and slow-release nutrients, promoting healthy potato growth without synthetic chemicals.
Signs of Nutrient Deficiency
Monitor potato plants for signs of nutrient deficiency, such as yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or delayed flowering. Conduct a soil test to identify specific nutrient deficiencies and adjust fertilizer applications accordingly.
Watering After Fertilization
After applying fertilizer, water the potato plants deeply to help nutrients reach the root zone. Consistent moisture is essential for optimal nutrient uptake and tuber development.
Conclusion
By providing the right balance of nutrients throughout the potato growing season, you can ensure strong plant growth, disease resistance, and a plentiful potato harvest. Remember to tailor your fertilization approach based on soil conditions, plant needs, and environmental factors for successful potato cultivation. Enjoy harvesting delicious, homegrown potatoes from your garden!
Go and turn on towards organic farming to save future and thire save childs:
Elevate Plant Growth with Premium Bone Powder – Buy Now!
Organic Cow Dung Compost: Transform Your Garden Naturally
Premium Humic Acid for Healthy Plants | Enhance Soil & Boost Growth
Boost Plant Growth Naturally with Mustard Cake | Organic Fertilizer
Transform Your Garden with NPK Fertilizer | Boost Growth by 30%
Premium Perlite for Enhanced Gardening | Buy Now
Live Earthworms with Enhance Your Garden (soil health)
1 Neem Khali: Unveiling the Wonders of Nature
1Transform your garden with vermiwash-buy now
1 Premium quality Vermicompost [ केचुआ खाद ]
Follow us: