No products in the cart.
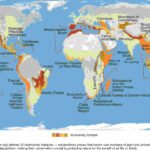
Exploring the Worlds Biological Hotspots
Biological Hotspots in the World
In our vast and diverse world, there are unique regions known as Worlds Biological Hotspots. These areas are teeming with life, housing an incredible variety of plants, animals, and ecosystems. Exploring these hotspots offers us a glimpse into the planet’s rich biodiversity and the importance of conserving it. In this article, we’ll take a journey through some of the most fascinating biological hotspots on Earth.

Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
|---|---|
| 1 | Introduction to Worlds Biological Hotspots |
| 2 | The Importance of Worlds Biological Hotspots |
| 3 | The Amazon Rainforest |
| 4 | The Congo Basin |
| 5 | The Eastern Himalayas |
| 6 | Madagascar |
| 7 | The Mediterranean Basin |
| 8 | The Caribbean Islands |
| 9 | The Coral Triangle |
| 10 | The Western Ghats |
| 11 | The California Floristic Province |
| 12 | The Atlantic Forest |
| 13 | Threats to Worlds Biological Hotspots |
| 14 | Conservation Efforts |
| 15 | Conclusion |
Introduction to Worlds Biological Hotspots
Worlds Biological Hotspots are regions with a high level of biodiversity that are under threat from human activities. Imagine these places as nature’s treasure chests, brimming with rare and unique species found nowhere else on Earth. These hotspots are crucial for maintaining global biodiversity, yet they cover only a small fraction of the planet’s surface. Understanding and protecting these areas is essential for the health of our planet.
The Importance of Worlds Biological Hotspots
Why should we care about biological hotspots? Well, they are not just home to a vast array of species, but they also provide vital ecosystem services that benefit humans. These include clean air and water, pollination of crops, and sources of medicine. Preserving these areas ensures that we maintain these essential services and helps combat climate change.
The Amazon Rainforest
The Amazon Rainforest, often referred to as the “lungs of the Earth,” is one of the most well-known Worlds Biological Hotspots. This vast forest spans across nine countries in South America and is home to an astounding variety of species. From colorful birds and elusive jaguars to countless plant species, the Amazon’s biodiversity is unparalleled.
Flora and Fauna
The Amazon is a sanctuary for about 390 billion individual trees belonging to 16,000 species. It’s also a habitat for over 2.5 million insect species, tens of thousands of plants, and a diverse range of animals, including the iconic Amazon River dolphin.
Conservation Challenges
Despite its importance, the Amazon faces significant threats from deforestation, mining, and agriculture. These activities not only destroy habitats but also contribute to climate change by releasing stored carbon dioxide.
The Congo Basin
The Congo Basin in Central Africa is another crucial Worlds Biological Hotspots. It’s the second-largest tropical rainforest in the world and plays a vital role in regulating the Earth’s climate.
Unique Species
Home to gorillas, elephants, and an array of bird species, the Congo Basin is rich in wildlife. It also houses the critically endangered bonobo, a close relative of humans.
Human Impact
Logging, poaching, and political instability pose significant threats to the Congo Basin. Efforts to conserve this area are essential for protecting its unique biodiversity and the indigenous communities that depend on it.
The Eastern Himalayas
Stretching across Bhutan, northeastern India, and southern Tibet, the Eastern Himalayas are a treasure trove of biodiversity. This region boasts a wide range of ecosystems, from subtropical forests to alpine meadows.
Biodiversity Highlights
The Eastern Himalayas are home to rare species like the red panda, snow leopard, and one-horned rhinoceros. The region also has a rich diversity of plant life, including many medicinal plants.
Conservation Issues
Climate change and habitat loss are significant challenges in the Eastern Himalayas. Protecting this area is crucial for the survival of its unique species and the well-being of local communities.
Madagascar
Madagascar, an island nation off the southeastern coast of Africa, is famous for its incredible biodiversity. Approximately 90% of its wildlife is found nowhere else on Earth.
Endemic Species
Lemurs, chameleons, and baobab trees are just a few examples of Madagascar’s unique species. The island’s isolation has allowed these species to evolve in remarkable ways.
Threats to Biodiversity
Deforestation, hunting, and climate change threaten Madagascar’s ecosystems. Conservation efforts are vital to protect the island’s unique species and habitats.
The Mediterranean Basin
The Mediterranean Basin, encompassing parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, is another Worlds Biological Hotspots This region is known for its diverse plant life and unique ecosystems.
Flora and Fauna
The Mediterranean Basin is home to around 25,000 plant species, many of which are endemic. It also supports a variety of animals, including the Iberian lynx and the Mediterranean monk seal.
Human Activities
Urbanization, agriculture, and tourism pose significant threats to the Mediterranean Basin. Sustainable practices are necessary to balance human needs with conservation.
The Caribbean Islands
The Caribbean Islands are renowned for their stunning landscapes and rich biodiversity. These islands host a variety of ecosystems, from rainforests to coral reefs.
Marine and Terrestrial Life
The Caribbean is home to unique species such as the West Indian manatee and the Caribbean monk seal. The region’s coral reefs are among the most diverse in the world, supporting a wide range of marine life.
Environmental Pressures
Overfishing, pollution, and climate change threaten the Caribbean’s biodiversity. Conservation initiatives are crucial for protecting both terrestrial and marine ecosystems.
The Coral Triangle
The Coral Triangle, located in the western Pacific Ocean, is often called the “Amazon of the Seas” due to its incredible marine biodiversity.
Marine Biodiversity
This area boasts over 600 species of coral and is home to 37% of the world’s coral reef fish species. The Coral Triangle is a vital breeding ground for marine life, including sea turtles and sharks.
Conservation Challenges
Overfishing, climate change, and destructive fishing practices pose significant threats to the Coral Triangle. Efforts to promote sustainable fishing and marine conservation are essential for preserving this underwater treasure.
The Western Ghats
The Western Ghats, a mountain range in India, is a hotspot of biodiversity and one of the most important areas for conservation in the country.
Flora and Fauna
This region is home to a variety of endemic species, including the Nilgiri tahr, lion-tailed macaque, and numerous plant species. The Western Ghats also support a range of ecosystems, from tropical rainforests to grasslands.
Threats and Conservation
Deforestation, agriculture, and infrastructure development threaten the Western Ghats. Conservation efforts focus on protecting habitats and promoting sustainable development practices.
The California Floristic Province
The California Floristic Province, located in the United States, is known for its unique plant species and diverse ecosystems.
Plant Diversity
This region is home to around 3,500 plant species, many of which are found nowhere else. The California poppy, the state’s iconic flower, is just one example of its rich flora.
Conservation Issues
Urbanization, agriculture, and climate change pose significant threats to this area. Conservation efforts aim to protect habitats and promote sustainable land use practices.
The Atlantic Forest
The Atlantic Forest, stretching along the eastern coast of Brazil, is another vital Worlds Biological Hotspots
Unique Ecosystems
This region supports a wide range of ecosystems, from coastal forests to inland rainforests. It’s home to many endemic species, including the golden lion tamarin and the maned three-toed sloth.
Human Impact
Deforestation, agriculture, and urbanization have significantly reduced the Atlantic Forest’s size. Conservation efforts focus on habitat restoration and protection.
Threats to Worlds Biological Hotspots
Worlds Biological Hotspots face numerous threats, primarily due to human activities. Deforestation, habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, and overexploitation of resources are some of the main challenges. These threats not only endanger the species living in these hotspots but also disrupt the ecosystem services they provide.
Conservation Efforts
Protecting Worlds Biological Hotspots requires a combination of strategies, including establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable development, and engaging local communities in conservation efforts. International cooperation and funding are also crucial for effective conservation. Organizations like the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and Conservation International are actively working to preserve these vital regions.
Conclusion
Worlds Biological Hotspots are the jewels of our planet, harboring incredible biodiversity and providing essential ecosystem services. Protecting these areas is not just about saving species; it’s about preserving the natural systems that sustain life on Earth. By raising awareness and supporting conservation efforts, we can ensure that these hotspots continue to thrive for generations to come.
FAQs
1. What is a biological hotspot?
A biological hotspot is a region with a high level of biodiversity that is under threat from human activities. These areas are rich in unique species and ecosystems but face significant environmental pressures.
2. Why are biological hotspots important?
Biological hotspots are crucial for maintaining global biodiversity. They provide essential ecosystem services, such as clean air and water, pollination, and sources of medicine, which are vital for human well-being.
3. What are the main threats to biological hotspots?
The main threats to biological hotspots include deforestation, habitat destruction, climate change, pollution, and overexploitation of resources. These activities endanger species and disrupt ecosystem services.
4. How can we protect biological hotspots?
Protecting biological hotspots involves establishing protected areas, promoting sustainable development, engaging local communities in conservation efforts, and supporting international cooperation and funding for conservation initiatives.
5. Can biological hotspots recover from damage?
With effective conservation efforts, biological hotspots can recover from damage. Restoration projects, habitat protection, and sustainable practices can help restore ecosystems and support the return of native species.
Go and turn on towards organic farming to save future and thire save childs:
Elevate Plant Growth with Premium Bone Powder – Buy Now!
Organic Cow Dung Compost: Transform Your Garden Naturally
Premium Humic Acid for Healthy Plants | Enhance Soil & Boost Growth
Boost Plant Growth Naturally with Mustard Cake | Organic Fertilizer
Transform Your Garden with NPK Fertilizer | Boost Growth by 30%
Premium Perlite for Enhanced Gardening | Buy Now
Live Earthworms with Enhance Your Garden (soil health)
1 Neem Khali: Unveiling the Wonders of Nature
1Transform your garden with vermiwash-buy now
1 Premium quality Vermicompost [ केचुआ खाद ]
Follow us:



