No products in the cart.

The National Centre for Organic and Natural Farming
The National Centre for Organic and Natural Farming: Cultivating a Sustainable Future
In today’s world, where concerns about food safety, environmental sustainability, and personal health are paramount, the concept of organic and natural farming is gaining increasing attention. The establishment of national centers dedicated to promoting and advancing these practices is a pivotal step towards ensuring a healthier and more sustainable future for agriculture. In this article, we’ll delve into the significance of a National Centre for Organic and Natural Farming (NCOF), exploring its role in revolutionizing agricultural practices and fostering a harmonious relationship between nature and food production.

Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
|---|---|
| 1 | Understanding Organic and Natural Farming |
| 2 | Importance of Establishing a national centre for organic and natural farming |
| 3 | Objectives of the national centre for organic and natural farming |
| 4 | Key Functions and Initiatives |
| 5 | Training and Capacity Building |
| 6 | Research and Development |
| 7 | Promoting Sustainable Practices |
| 8 | Collaborations and Partnerships |
| 9 | Impact on Farmers and Consumers |
| 10 | Future Prospects and Expansion |
| 11 | Conclusion |
| 12 | FAQs |
1. Understanding national centre for organic and natural farming
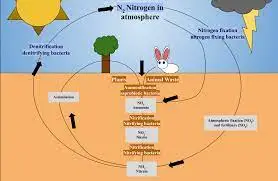
Organic and natural farming revolves around cultivating crops and raising livestock using natural methods, without synthetic chemicals or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). This approach emphasizes soil health, biodiversity, and animal welfare, producing food that is free from harmful residues and supports ecological balance.
2. Importance of Establishing a national centre for organic and natural farming
The establishment of a National Centre for Organic and Natural Farming (NCOF) is crucial in promoting and mainstreaming sustainable agricultural practices across the country. It serves as a hub for research, education, and training, driving innovation and awareness in the agricultural sector.
3. Objectives of the national centre for organic and natural farming
The primary objectives of an NCOF include:
- Advancing Research: Conducting scientific studies to enhance organic farming techniques.
- Educational Outreach: Providing training and workshops to farmers and stakeholders.
- Policy Advocacy: Influencing agricultural policies to support organic farming practices.
4. Key Functions and Initiatives
The NCOF undertakes several key functions and initiatives:
- Certification Programs: Establishing standards and certification for organic produce.
- Technology Transfer: Facilitating the adoption of sustainable farming technologies.
- Market Development: Promoting organic products and market linkages for farmers.
5. Training and Capacity Building
One of the pivotal roles of the NCOF is training and capacity building. By offering workshops, demonstrations, and skill development programs, the center empowers farmers to transition to organic and national centre for organic and natural farming methods effectively.
6. Research and Development
The NCOF invests in research and development to optimize organic farming techniques, improve crop yields, and mitigate environmental impacts. This research contributes to the broader understanding and adoption of sustainable agricultural practices.
7. Promoting Sustainable Practices
Through awareness campaigns and demonstrations, the NCOF encourages the adoption of sustainable farming practices that preserve soil health, conserve water resources, and reduce chemical inputs.
8. Collaborations and Partnerships
The center collaborates with national and international organizations, academia, and industry stakeholders to leverage expertise, resources, and best practices in organic farming.
9. Impact on Farmers and Consumers
The NCOF positively impacts farmers by providing them with lucrative market opportunities, reducing input costs, and ensuring healthier produce for consumers. Consumers benefit from access to safe, nutritious, and chemical-free food.
10. Future Prospects and Expansion
As awareness about organic farming grows, the NCOF’s role will become increasingly pivotal. There is potential for expanding its reach, establishing regional centers, and integrating organic farming into mainstream agricultural policies.
11. Conclusion
In conclusion, the establishment of a National Centre for Organic and national centre for organic and natural farming represents a transformative step towards sustainable agriculture. By promoting organic practices, the NCOF contributes to environmental conservation, food safety, and the overall well-being of farmers and consumers alike.
Natural farming vs organic farming
Natural farming and organic farming are both sustainable agricultural methods that prioritize environmental health and the production of healthy, chemical-free food. While they share similar goals, there are notable differences between the two approaches.
national centre for organic and natural farming, also known as nature farming or do-nothing farming, is a holistic approach that emphasizes working with natural processes and biodiversity to cultivate crops. It was popularized by Japanese farmer and philosopher Masanobu Fukuoka. The core principles of natural farming include:
- Minimal Intervention: Natural farmers believe in minimal interference with nature’s processes. They avoid tilling, weeding, and using chemical fertilizers or pesticides.
- Cover Cropping: Cover crops are used to improve soil fertility and prevent erosion. These crops are often legumes that fix nitrogen in the soil.
- Mulching: Mulching with straw or other organic materials helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and improve soil structure.
- Crop Diversity: Natural farmers encourage biodiversity by growing a variety of crops together, mimicking natural ecosystems.
national centre for organic and natural farming focuses on enhancing the health of the entire farm ecosystem rather than maximizing yields through intensive practices.
Organic Farming: Organic farming is a regulated agricultural system that emphasizes the use of natural inputs and prohibits the use of synthetic chemicals, GMOs, and irradiation. The principles of organic farming include:
- Soil Health: Organic farmers prioritize soil health through practices such as crop rotation, composting, and using organic fertilizers like manure or compost.
- Pest and Disease Management: Organic farmers use natural methods like crop rotation, beneficial insects, and physical barriers to manage pests and diseases.
- Certification: Organic farming is regulated by certification bodies that verify compliance with organic standards, ensuring the integrity of organic products.
Organic farming aims to produce food that is free from synthetic chemicals and GMOs, promoting biodiversity and reducing the environmental impact of agriculture.
Key Differences:
- Philosophy: Natural farming is more of a philosophy that advocates for working in harmony with nature, while organic farming is a regulated agricultural system with specific standards.
- Intervention: Natural farming involves minimal intervention and emphasizes observing and learning from natural systems, whereas organic farming allows for more intervention but restricts the use of synthetic inputs.
- Certification: Organic farming requires certification to verify compliance with organic standards, while natural farming is often practiced without formal certification or regulation.
In summary, both national centre for organic and natural farmingand organic farming promote sustainable agriculture, but they differ in their approaches and underlying philosophies. Natural farming emphasizes minimal intervention and working with natural processes, while organic farming adheres to specific standards and regulations to ensure the production of chemical-free food. Each approach offers unique benefits and challenges, contributing to the diversity of sustainable farming practices worldwide.
similarities between organic and natural farming
Organic farming and natural farming share several similarities as sustainable agricultural methods that prioritize environmental health and the production of healthy, chemical-free food. Here are some key similarities between organic and natural farming:
- Avoidance of Synthetic Chemicals: Both organic and national centre for organic and natural farming methods emphasize avoiding synthetic chemicals such as pesticides, herbicides, and synthetic fertilizers. Instead, they rely on natural inputs like compost, cover crops, and beneficial insects to manage pests and enhance soil fertility.
- Focus on Soil Health: Both farming methods prioritize soil health by using practices that improve soil structure, enhance soil fertility, and promote microbial activity. Techniques like composting, mulching, and crop rotation are common in both organic andnational centre for organic and natural farming to maintain soil health without chemical inputs.
- Promotion of Biodiversity: Organic and national centre for organic and natural farming encourage biodiversity within the farming system. By planting diverse crops, incorporating cover crops, and creating habitats for beneficial insects and wildlife, both methods contribute to ecological balance and resilience in agricultural landscapes.
- Holistic Approach: Both farming methods take a holistic approach to agriculture, considering the entire farm ecosystem rather than focusing solely on crop production. They aim to work in harmony with nature, leveraging natural processes and reducing reliance on external inputs.
- Emphasis on Sustainability: Both organic and national centre for organic and natural farming prioritize sustainability by minimizing environmental impacts such as soil erosion, water pollution, and habitat destruction. These methods aim to create resilient farming systems that can adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Healthy Food Production: Both organic and national centre for organic and natural farming methods aim to produce healthy, nutritious food without synthetic residues or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). By avoiding chemical inputs and promoting soil health, these methods contribute to the production of food that is safer and more wholesome for consumers.
- Community and Consumer Awareness: Both organic and national centre for organic and natural farming methods often involve building strong connections with local communities and consumers who value sustainable and environmentally friendly food production. Farmers practicing these methods often engage in direct marketing or community-supported agriculture (CSA) to connect with consumers who appreciate their farming practices.
In summary, organic farming and national centre for organic and natural farming share common principles and goals related to sustainability, soil health, biodiversity, and the production of healthy food. While there are differences in specific practices and philosophies, both methods represent important alternatives to conventional, chemically intensive agriculture, promoting environmentally responsible farming practices that benefit farmers, consumers, and the planet.
difference between organic farming and conventional farming
The difference between organic farming and conventional farming lies in their approaches, practices, and philosophies regarding agricultural production. Here are the key distinctions between these two farming methods:
- Use of Synthetic Inputs:
- Conventional Farming: Conventional farming relies heavily on synthetic inputs such as chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides to maximize crop yields and control pests and diseases.
- Organic Farming: Organic farming avoids synthetic inputs and instead utilizes natural and organic methods for soil fertility management, pest and disease control, and weed management. Organic farmers use compost, cover cropping, and natural pest predators to maintain soil health and crop productivity.
- Approach to Soil Health:
- Conventional Farming: Conventional farming often practices intensive tillage, which can lead to soil erosion, degradation, and loss of organic matter. Synthetic fertilizers may provide immediate nutrients but can degrade soil health over time.
- Organic Farming: Organic farming prioritizes soil health by focusing on practices that improve soil structure, enhance microbial activity, and promote nutrient cycling. Techniques like crop rotation, mulching, and composting are used to maintain soil fertility and structure.
- Pest and Disease Management:
- Conventional Farming: Conventional farming relies on chemical pesticides to control pests and diseases, which can lead to pesticide resistance, harm beneficial insects, and pose risks to human health and the environment.
- Organic Farming: Organic farming uses integrated pest management (IPM) techniques such as crop rotation, companion planting, and the introduction of beneficial insects to manage pests and diseases naturally without synthetic chemicals.
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs):
- Conventional Farming: Conventional farming may incorporate genetically modified (GM) crops that are engineered for traits such as herbicide resistance or pest resistance.
- Organic Farming: Organic farming prohibits the use of GMOs. Organic certification standards require the exclusion of genetically modified organisms in all stages of production, including seeds and inputs.
- Regulations and Certification:
- Conventional Farming: Conventional farming is not subject to specific regulations related to synthetic inputs or farming practices, apart from general agricultural regulations.
- Organic Farming: Organic farming is regulated by national or international standards that define specific practices, inputs, and processes required for organic certification. Farms must undergo inspection and certification by accredited certifying bodies to be recognized as organic.
- Environmental Impact:
- Conventional Farming: Conventional farming practices can contribute to environmental issues such as soil erosion, water pollution from runoff, and loss of biodiversity due to chemical use.
- Organic Farming: Organic farming promotes environmental sustainability by minimizing chemical inputs, preserving soil health, conserving water resources, and promoting biodiversity through ecological farming practices.
In summary, organic farming and conventional farming represent distinct approaches to agricultural production, with organic farming emphasizing natural methods, soil health, biodiversity, and environmental stewardship, while conventional farming relies on synthetic inputs and intensive practices to maximize yields. Each approach has implications for food safety, environmental sustainability, and the overall health of agricultural ecosystems.
advantages of conventional farming
Conventional farming, characterized by the use of synthetic inputs and modern agricultural technologies, offers several advantages that have contributed to its widespread adoption and efficiency in food production:
- Higher Yields: Conventional farming practices, such as the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, genetically modified organisms (GMOs), and mechanized equipment, often result in higher crop yields compared to traditional or organic farming methods. This increased productivity helps meet the growing global demand for food.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Conventional farming can be more cost-effective in terms of labor and inputs. Synthetic fertilizers and pesticides are generally less expensive than organic alternatives, and mechanization reduces the need for manual labor, leading to economies of scale and lower production costs.
- Efficient Land Use: Conventional farming methods often involve intensive production techniques that maximize the use of available land. Through practices like monocropping and precision agriculture, farmers can efficiently utilize land resources to produce larger quantities of food.
- Technological Innovation: Conventional farming relies on technological advancements such as GMOs, precision agriculture, and automated machinery. These innovations enable farmers to monitor crops more effectively, optimize inputs, and respond quickly to changes in weather or market conditions.
- Global Food Security: Conventional farming plays a critical role in ensuring global food security by consistently producing large quantities of affordable food. The ability to scale production and respond to market demands helps stabilize food supplies and prices.
- Accessibility: Conventional farming methods are more accessible to farmers in terms of knowledge, infrastructure, and resources. The availability of synthetic inputs, agricultural machinery, and extension services facilitates adoption and implementation of conventional practices.
- Consistency and Predictability: Conventional farming practices often lead to more predictable outcomes in terms of crop yields and quality. The use of synthetic inputs helps control pests and diseases, reducing crop losses and ensuring consistent production.
- Adaptability to Market Demands: Conventional farming systems are often more adaptable to market demands and consumer preferences. Farmers can adjust production practices and crop varieties to meet specific market requirements for size, appearance, and shelf-life.
- Supports Agribusiness and Rural Economies: Conventional farming contributes to the growth of agribusiness sectors such as seed production, chemical manufacturing, and machinery sales. This supports rural economies by generating employment and stimulating economic development.
- Scaling for Large-Scale Production: Conventional farming methods are well-suited for large-scale production systems, allowing farmers to manage extensive acreages efficiently and produce commodities for processing and distribution on a commercial scale.
Despite these advantages, it’s important to acknowledge that conventional farming also poses challenges related to environmental sustainability, soil health, biodiversity loss, and human health impacts from chemical exposure. Balancing the benefits of conventional agriculture with sustainable practices and environmental stewardship remains a critical focus for the future of global food production.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the role of a National Centre for Organic and Natural Farming?
The NCOF plays a vital role in advancing research, providing training, and advocating for policies that support organic and natural farming practices.
2. How does organic farming benefit farmers?
Organic farming reduces input costs, offers premium prices for organic produce, and enhances soil fertility, leading to sustainable farming practices.
3. Are organic products more expensive?
While organic products may initially seem more expensive due to higher production costs, they offer long-term benefits in terms of health and environmental impact.
4. How can consumers support organic farming?
Consumers can support organic farming by purchasing organic products, advocating for sustainable agriculture policies, and spreading awareness about the benefits of organic farming.
5. Is organic farming better for the environment?
Yes, organic farming promotes biodiversity, reduces chemical pollution, conserves water, and maintains soil fertility, making it a more sustainable choice for the environment.
In essence, the establishment of a National Centre for Organic and Natural Farming signifies a paradigm shift towards a more sustainable and ecologically conscious approach to agriculture. Through research, education, and advocacy, these centers are instrumental in shaping the future of food production towards a healthier and greener tomorrow.
Go and turn on towards organic farming to save future and thire save childs:
Elevate Plant Growth with Premium Bone Powder – Buy Now!
Organic Cow Dung Compost: Transform Your Garden Naturally
Premium Humic Acid for Healthy Plants | Enhance Soil & Boost Growth
Boost Plant Growth Naturally with Mustard Cake | Organic Fertilizer
Transform Your Garden with NPK Fertilizer | Boost Growth by 30%
Premium Perlite for Enhanced Gardening | Buy Now
Live Earthworms with Enhance Your Garden (soil health)
1 Neem Khali: Unveiling the Wonders of Nature
1Transform your garden with vermiwash-buy now
1 Premium quality Vermicompost [ केचुआ खाद ]
Follow us: