No products in the cart.

“Sustainable Farming Practices: Benefits, Techniques, and Examples”
Sustainable Farming Practices: A Guide to Eco-Friendly Agriculture
Introduction
In today’s world, sustainable farming is more than just a buzzword; it’s a crucial practice that ensures our planet’s health for future generations. But what does sustainable farming really mean, and how can it benefit us all? Let’s dive into the world of eco-friendly agriculture and discover how simple changes in farming practices can make a big difference.
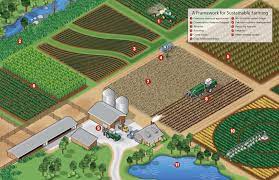
Table of Contents
| Sr# | Headings |
|---|---|
| 1 | What is Sustainable Farming? |
| 2 | Benefits of Sustainable Farming |
| 3 | Organic Farming vs. Sustainable Farming |
| 4 | Practices and Techniques |
| 5 | Crop Rotation and Soil Health |
| 6 | Water Conservation Techniques |
| 7 | Integrated Pest Management (IPM) |
| 8 | Agroforestry and Biodiversity |
| 9 | Sustainable Livestock Management |
| 10 | Sustainable Farming Examples |
| 11 | Challenges in Sustainable Farming |
| 12 | Government Policies and Sustainable Agriculture |
| 13 | Future Trends in Sustainable Agriculture |
| 14 | Conclusion |
| 15 | FAQs |
1. What is Sustainable Farming?
Sustainable farming is a method of agriculture that focuses on producing food in a way that preserves the environment, public health, and animal welfare. Unlike conventional farming, which can deplete soil nutrients and rely heavily on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, sustainable farming aims to use techniques that maintain soil fertility and support biodiversity.
2. Benefits of Sustainable Farming
Sustainable farming offers numerous benefits both to the environment and to consumers. By reducing the use of harmful chemicals and promoting healthy soil, sustainable practices can improve crop yields over the long term and protect natural ecosystems.
Key Points:
- Environmental Conservation: Reduces soil erosion and improves water quality.
- Healthier Food Options: Lowers exposure to pesticides and chemicals.
- Economic Resilience: Builds long-term resilience in farming communities.
3. Organic Farming vs. Sustainable Farming
While both organic and sustainable farming focus on environmental stewardship, they differ in their specific practices. Organic farming strictly prohibits the use of synthetic chemicals, whereas sustainable farming is a broader concept that includes responsible land management and conservation practices.
4. Practices and Techniques
Crop Rotation and Soil Health
Crop rotation involves growing different types of crops in the same area over sequential seasons. This practice helps maintain soil fertility, reduce soil erosion, and prevent pests and diseases.
Water Conservation Techniques
Implementing drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting are crucial in sustainable farming to conserve water resources and reduce the strain on local water supplies.
Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM combines biological, cultural, and mechanical methods to manage pests effectively, minimizing the use of chemical pesticides.
5. Agroforestry and Biodiversity
Agroforestry integrates trees and shrubs into farming systems, enhancing biodiversity, improving soil health, and providing additional income sources for farmers.
6. Sustainable Livestock Management
Practices like rotational grazing and reduced antibiotic use in livestock help maintain animal welfare and minimize environmental impact.
7. Sustainable Farming Examples
Examples of sustainable farming include permaculture, community-supported agriculture (CSA), and vertical farming, each tailored to different environmental and economic conditions.
8. Challenges in Sustainable Farming
Despite its benefits, sustainable farming faces challenges such as initial costs, knowledge gaps, and policy support.
9. Government Policies and Sustainable Agriculture
Governments worldwide are increasingly promoting sustainable agriculture through subsidies, regulations, and research funding.
10. Future Trends in Sustainable Agriculture
The future of sustainable agriculture lies in technological innovations, data-driven farming practices, and global collaboration.
11. Conclusion
In conclusion, sustainable farming practices are vital for our planet’s future. By adopting these practices, we can protect the environment, enhance food security, and promote healthier lifestyles for everyone.
12. FAQs
1. What are the main goals of sustainable farming?
The main goals are to protect the environment, promote economic viability, and ensure healthy food production.
2. How does sustainable farming help in conserving water?
Through practices like drip irrigation and rainwater harvesting, sustainable farming minimizes water usage and promotes efficient water management.
3. What are the challenges of adopting sustainable farming practices?
Challenges include initial costs, knowledge gaps, and the need for supportive government policies.
4. How does sustainable farming benefit farmers?
It benefits farmers by improving soil health, reducing input costs, and providing long-term economic stability.
5. Is organic farming the same as sustainable farming?
No, while they share some principles, sustainable farming encompasses broader conservation and land management practices beyond the use of synthetic chemicals.
Go and turn on towards organic farming to save future and thire save childs:
Elevate Plant Growth with Premium Bone Powder – Buy Now!
Organic Cow Dung Compost: Transform Your Garden Naturally
Premium Humic Acid for Healthy Plants | Enhance Soil & Boost Growth
Boost Plant Growth Naturally with Mustard Cake | Organic Fertilizer
Transform Your Garden with NPK Fertilizer | Boost Growth by 30%
Premium Perlite for Enhanced Gardening | Buy Now
Live Earthworms with Enhance Your Garden (soil health)
1 Neem Khali: Unveiling the Wonders of Nature
1Transform your garden with vermiwash-buy now
1 Premium quality Vermicompost [ केचुआ खाद ]
Follow us:
Tagged Insustainable farming practices


